Psychedelic mushrooms, commonly referred to as magic mushrooms, are mushrooms containing psychoactive ingredients, which also result in psychotropic effects among consumers. This type of mushroom can also be used to manage conditions like anxiety, stress, and PTSD. They are available for sale in multiple online dispensaries.
Buying from a trusted magic mushrooms dispensary takes the anxiety out of sourcing powerful hallucinogenics. Take your time to identify the right platforms to purchase your magic mushrooms.
The psychedelic psilocybe mushrooms are found all over the world. Therefore, it can be assumed that the shamanic cultures in the various parts of the world also knew about the effectiveness of mushrooms and took them in a ritualistic setting.
The Psychedelic Chemistry of Magic Mushrooms
All mushrooms that belong to the psilocybin complex have the psychedelic molecules psilocybin, psilocin, baeocystin, and norbaeocystin, or at least one of the active ingredients mentioned. All molecules belong to the indole alkaloids and the chemical class of tryptamines. Therefore, they are related to the body’s own substances, serotonin, which is why the substances also bind to those receptors in the human body. Let’s look at the individual molecules in detail.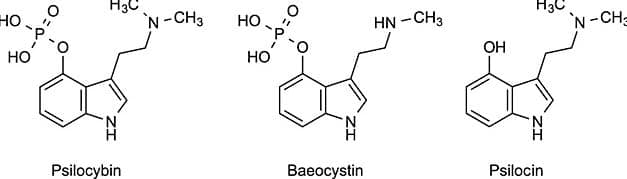
Psilocybin
The indolamine psilocybin is basically not the active ingredient responsible for the entheogenic experience of magic mushrooms. In truth, a phosphate group splits off from the molecule immediately after taking psilocybin – and psilocybin becomes psilocin, the actual active substance. Psilocybin is a so-called phosphoric acid ester. A psilocybin or psilocin experience usually lasts between three and five or six hours. As a rule, however, the duration of the psychedelic journey is exactly four hours.
Psilocin
The indolamine psilocin is a psychoactive ingredient that enables profound entheogenic experiences. Psilocin occurs as a natural substance in various mushrooms but is metabolized in the human (and animal) body by splitting off phosphoric acid from psilocybin. The exact dosage and duration of action apply as for psilocybin.
Baeocystin
The indolamine baeocystin is not only related to psilocybin and psilocin, but it is probably the natural precursor of psilocybin. Perhaps baeocystin is derived from tryptophan. Baeocystin has weak psychoactive properties, but the molecule may only serve as an intermediate stage in psilocin’s natural synthesis.
Norbaeocystin
 The indolamine norbaeocystin has been known since 1968. It is believed to have mild psychoactive properties like baeocystin. However, it is also possible that norbaeocystin is not psychoactive per se but that the molecule is only an intermediate product within the biosynthesis of psilocybin/psilocin.
The indolamine norbaeocystin has been known since 1968. It is believed to have mild psychoactive properties like baeocystin. However, it is also possible that norbaeocystin is not psychoactive per se but that the molecule is only an intermediate product within the biosynthesis of psilocybin/psilocin.
Synthetic Analogs
There are two synthetic psilocybin analogs. These have the cryptic names CZ-74 (or 4-OH-DET) and CY-19 (4-phosphoroxy-N, N-DET). Both substances act like psilocin, only for a shorter time, and were once used with great success in psychedelically supported psychotherapy.

